The unique climate characteristics of the US southern Great Plains allow producers to use wheat as a forage and grain crop (dual-purpose), potentially increasing overall profitability compared to grain-only or forage-only systems. The date of grazing termination is an important factor in determining wheat’s recovery potential and ability to produce grain. First hollow stem (FHS) is the optimal time to remove cattle from wheat pastures to protect grain yield potential.
What is the first hollow stem (FHS) stage of wheat development?
Before the wheat leaf sheaths become erect after spring green-up, the developing growing point below the soil surface will soon begin to form a tiny head. Although the head is quite small at this point, it has already established some important yield components. At this stage, the maximum potential number of spikelets is determined. Sufficient nitrogen (N) should already be available in the root zone at this growth stage to maximize the potential number of seeds per head.
Once the embryo head has developed, the first internode will begin to elongate, pushing the head up through the leaf sheaths. This first internode will be hollow. This will be visible before you can actually feel the first node (joint, located just above the first internode).
FHS is the point at which a 1.5 cm (about half-inch) length of hollow stem can first be identified below the developing head (Figure 1). This length is roughly equivalent to a dime's diameter, making its identification in the field easier. FHS occurs when the developing head is still below the soil surface. This means that producers must dig plants out of the ground to measure it.
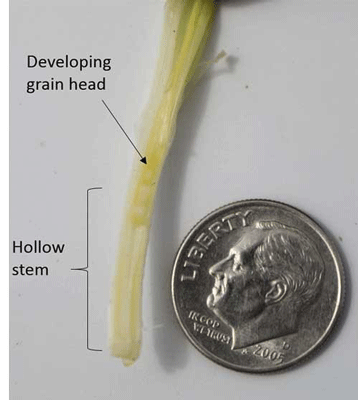
Figure 1. Wheat plant reaching the first hollow stem stage of growth, characterized by approximately 1.5 cm (or roughly the diameter of a dime) of hollow stem underneath the developing grain head. Photo by Romulo Lollato, K-State Research and Extension.
Assessing for first hollow stem
To look for FHS, start by digging up some plants from fields or areas that have not been grazed, such as field corners or just outside the fence. The date of FHS is variety- and field-specific, so it is important to sample each individual field. Select the largest tillers to examine, and slice the stem open from the crown area up. Look for the developing head, which will be very small. Next, see if you can find any hollow stem between the developing head and the crown area. The hollow stem is elongating if there is any separation between the growing point and crown. If that separation is 1.5 cm, the wheat plant is at FHS. FHS occurs between a few days to a week or more prior to jointing, depending on temperatures.
New tool for estimating first hollow stem in wheat
Winter wheat is beginning to break dormancy, and the Kansas Mesonet has introduced a new tool to help track the crop development: Wheat First Hollow Stem page. This page tracks soil temperature to calculate wheat growing degree days (GDD) associated with first hollow stem occurrence. This tool employs a wheat growth model developed by Oklahoma State University and the Oklahoma Mesonet, which was validated for wheat growing conditions experienced in south central Kansas during the 2016-2021 growing seasons. The model output provides the probability of the first hollow stem occurrence (current and historical) for early and late-maturing wheat varieties. More details for the tool are found here.
Yield losses from grazing past first hollow stem
Cattle should be removed if the wheat has reached FHS to prevent grain yield loss. Yield losses from grazing after FHS can range from 1% to 5% per day, depending on grazing intensity and the weather following cattle removal (Figure 2). If cattle removal is followed by cool, moist weather, yield losses will often average about 1% per day grazed after FHS; if weather is hot, dry, and harsh, yield losses of 5% per day or more can be expected. It is easy for producers to be late by a few days in removing livestock as they wait for obvious nodes and hollow stems to appear, and even the first few days can be significant.
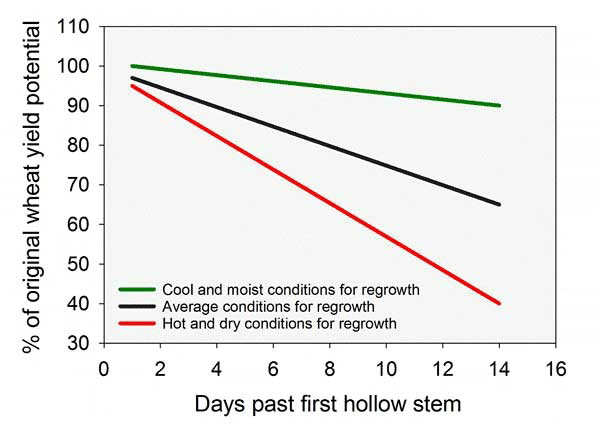
Figure 2. Percent of original wheat yield potential as affected by days of grazing past first hollow stem and weather conditions following grazing termination. Average yield losses by grazing for 14 days past first hollow stem ranged from 10% under favorable conditions to 60% under non-favorable conditions. Research conducted by Oklahoma State University (OSU) and published as K-State publication MF3375 and OSU publication PSS-2178.
Two things can occur when wheat is grazed too long: 1) fewer heads per acre because the primary tiller has been removed, and 2) smaller and lighter heads than expected because the leaf area has been removed. As cattle continue grazing, the wheat plant is stressed and begins to lose some of the tillers that would produce grain. A little later, if there are not enough photosynthates, the plant begins aborting the lower spikelets in the head or some of the florets on each head. Finally, if there is not enough photosynthate during grain filling, the seed size will be reduced, and if the stress is severe enough, some seeds will abort.
Air and soil temperatures during 2024
Crop development is mostly a function of available water, nutrients, and temperature. Nutrient availability is field-specific, and thus, we will not discuss it here. Water has been limited since the fall for the majority of the wheat-growing region of the state, which will likely slow down crop development. Likewise, average temperatures across most of Kansas were warmer than normal for the growing season this far, which is reflected in much of the crop across the state already having greened up (accelerating the progression toward the first hollow stem compared to most years). As temperatures increase and wheat grows more rapidly in the spring, producers should start thinking about when to pull cattle off pasture to protect grain yields. Soil temperatures may quickly warm as much of the state has dry soils. As the soils thaw, muddy conditions may also influence the decision to remove cattle in some areas.
For more information on managing wheat in dual-purpose systems, check the K-State Research and Extension publication MF3375 [PSS-2178 from Oklahoma State Extension], “Dual-purpose wheat: Management for forage and grain production” at https://www.bookstore.ksre.k-state.edu/pubs/MF3375.pdf.
Romulo Lollato, Wheat and Forages Specialist
lollato@ksu.edu