Herbicide-resistant grain sorghum has been a topic of conversation for several years. Now there are some questions among varieties available for next spring, with others getting closer to commercialization. This article will provide an overview of weed management in these herbicide-resistant grain sorghum systems. A preliminary summary of K-State weed control data in these production systems is included as Figure 1.
iGrowth – This is the trait that made news this summer. iGrowth grain sorghum has been developed by Advanta Seeds. These hybrids are resistant to the herbicide imazamox, which you might remember as Raptor or Beyond. The only formulation labeled for use in iGrowth sorghum Imiflex. UPL is seeking approval for pre-emergence and post-emergence applications of the product, however approval has not yet been granted.
Imazamox is a Group 2 (ALS-inhibiting) herbicide that controls a range of grass and broadleaf weeds. Key species controlled by imazamox include large crabgrass, foxtails, seedling johnsongrass, and shattercane, kochia, common lambsquarters, morningglories, nightshades, pigweeds, common sunflower, and velvetleaf. One concern with this technology is that resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides is found in kochia, Palmer amaranth, waterhemp, common sunflower, shattercane, and other weed species in Kansas. The widespread occurrence of resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides means that Imiflex should be combined with other effective herbicide modes of action to control resistant plants and slow the development additional herbicide resistance.
Inzen – Inzen grain sorghum hybrids are resistant to the herbicide nicosulfuron. The formulation approved for use in grain sorghum is called Zest, but nicosulfuron is also the active ingredient in Accent and a component of Pastora, Revulin Q, Steadfast, and others. This herbicide has received an EPA label for application to Inzen varieties that are between 4 and 20 inches tall.
Similar to Imiflex, Zest is a Group 2 herbicide. However, it is primarily active on grass weeds, including large crabgrass, foxtails, and sandburs. In addition to concerns regarding herbicide-resistant weeds, producers should be aware of long rotation intervals to some other crops including non-Inzen grain sorghum varieties.
Inzen sorghum and Zest are approved for commercial production with limited availability expected for 2021.
Double Team – This trait has been developed by S&W Seeds. Double Team grain sorghum hybrids are resistant to the herbicide quizalofop, which is the active ingredient in Assure II. ADAMA is currently awaiting EPA approval for the herbicide label that will be used in Double Team grain sorghum.
Quizalofop is a Group 1 (ACCase-inhibiting) herbicide that only controls grasses, but it is quite good at controlling species such as shattercane and crabgrass, which are often problematic in grain sorghum. Weed resistance to Group 1 herbicides is less common than group 2, but is still an important concern. Quizalofop resistance has not been reported in Kansas, but resistant biotypes of johnsongrass, giant foxtail, downy brome, and wild oat have been reported elsewhere in the US.
S&W anticipates expanded testing of Double Team sorghum for 2021, but has not provided an anticipated commercialization date.
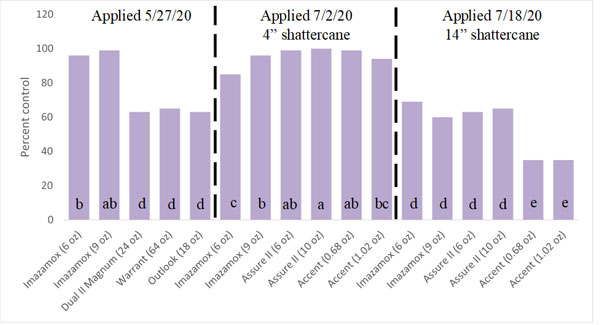
Figure 1. Shattercane control in a fallow area near Garden City KS. Weed control was recorded on July 24. Similar letters indicate similar weed control. Data from Currie and Geier, unpublished data.
Sarah Lancaster, Extension Weed Science Specialist
slancaster@ksu.edu
Randall Currie, Weed Scientist, KSU Southwest Research-Extension Center, Garden City
rscurrie@ksu.edu