In the current 2023 season, soybean acreage projections in Kansas are up compared to historical. For maximizing yields, there are key practices we cannot overlook. This article presents some tips on selecting the best planting date and maturity group across Kansas.
After considering the effects of genetic yield potential and the environment, planting date is one of the primary management practices under the farmer’s control that can highly influence soybean yields. In recent years, Kansas producers have been planting soybeans slightly earlier -- at the rate of about one-third-of-day per year. In 2022, the “50% planting date” mark was achieved around May 23 statewide (ahead of the 40% historical average) – with planting progress moving closer to mid-May if conditions are optimal at that time (USDA-Crop Progress Reports).
Planting dates and maturity group guidelines
Soybeans can be planted over a wide range of dates with adequate soil moisture conditions, although germination and emergence could be reduced and/or delayed in cool soils (less than 60°F). In the last few years, many farmers are anticipating soybean planting dates relative to the ones presented in Figure 1, in many situations planting soybeans before corn. The recommended maturity group varies across Kansas by area (Figure 2).
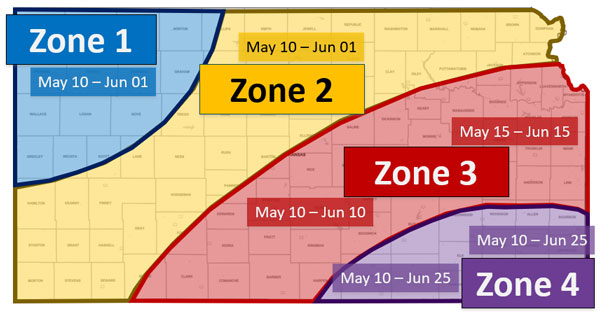
Figure 1. Recommended soybean planting dates under dryland conditions. K-State Research and Extension.
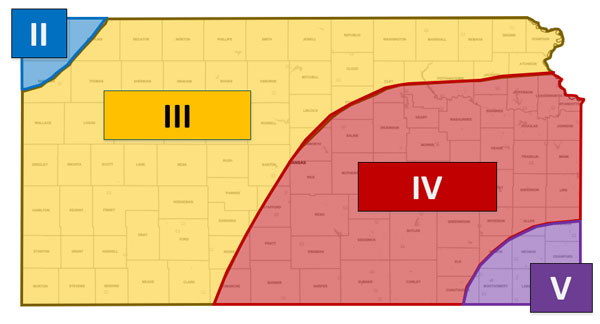
Figure 2. Recommended soybean maturity groups (II to V) across Kansas. K-State Research and Extension.
For Kansas, maximum soybean yield is reduced by 0.3 bu/a per day as planting dates get later in the season, with yield levels closer to 80-90 bu/a when planting in mid-April compared to 50 bu/a for planting in mid-July (Figure 3). These results highlight the importance of early planting for obtaining maximum yields and the overall yield penalty associated with delaying planting dates.
It is worth noting, however, that yields use to be considerably noisier (more variability) at the earlier planting dates. There is less variability and better yield “stability” for late-planted soybeans, although at lower potential yields (Figure 3).
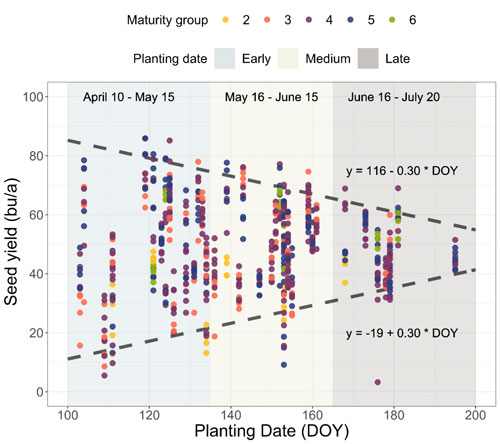
Figure 3. Soybean seed yields as a function of planting date from Early (mid-April to mid-May) to Medium (mid-May to mid-June) to Late (mid-June to mid-July) for a diverse set of maturity groups (from 2 to 6). Data from Ciampitti Lab, K-State Research and Extension.
This season, similar to 2022, farmers are planting soybeans earlier than usual, but a note of caution is that lower soil temperatures will reduce the speed of emergence and could compromise uniformity for soybeans. In addition, dry conditions in many areas of the state can further delay overall emergence and early season uniformity. A recent study completed by our research team showed that early-season plant-to-plant uniformity could compromise yields in soybeans, especially in low-yield environments (<35 bu/a). Similarly, at higher yield environments (where plants can express growth plasticity) such as in the east region of Kansas, a recent experiment from our previous growing season (2022) demonstrates that both early (May) and late planting (June) produced very similar average yield and variability (Figure 4).
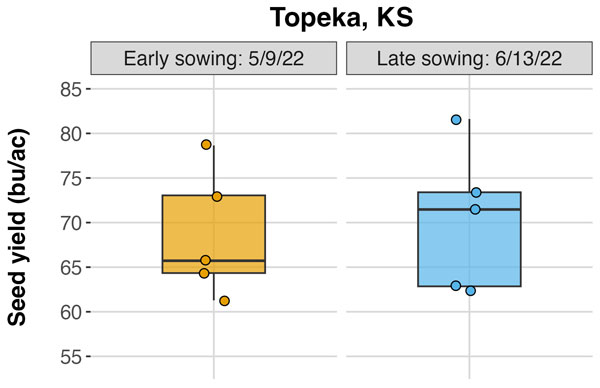
Figure 4. Soybean seed yield (bu/ac) comparing early (May) and late (June) at the Kansas River Valley Research Station, Topeka, KS. 2022 cropping season. Graph from Ciampitti Lab, K-State Research and Extension.
Final considerations
- Ultimately, weather patterns dictate soybean yields, especially under dryland conditions. There is no guarantee that any certain planting date will always work out best for soybean yields in Kansas. In fact, the distribution and amount of rainfall and the day/night temperature variations around flowering and during the grain-filling periods have significant impacts on soybean yields. Thus, when the risk of drought stress during the growing season is high, diversifying planting dates may be a good approach to consider.
- When planting early (many farmers are trying to plant soybeans before corn), the seed should be treated with a fungicide and insecticide. Selecting varieties with resistance to soybean cyst nematode and sudden death syndrome is advisable. Do not plant in soils that are too wet. Also, do not plant until soil temperatures are close to 60°F. If planted into soils cooler than 60°F, seedlings may eventually emerge but will have poor vigor.
- In drier areas of Kansas and on shallow soils, yields have been most consistent when planting soybeans in late May to early June. By planting during that window, soybeans will bloom and fill seed in August and early September, when nights are cooler and the worst of heat and drought stress is usually over.
Ignacio Ciampitti, Farming Systems
ciampitti@ksu.edu
Adrian Correndo, Postdoctoral Fellow
correndo@ksu.edu
Emmanuela van Versendaal, MS Student
evanversendaal@ksu.edu
Luiz Felipe Antunes de Almeida, MS Student
luizfelipeaa@ksu.edu
Tags: soybeans planting planting date