There are still many questions about row spacing for soybean production. In this article, we present a summary of recent research from K-State. From 2015 to 2017, a series of six On-Farm experiments were conducted across eastern and central Kansas (Figure 1).
For the 2015-16 seasons, four on-farm studies (a collaboration between K-State, Kansas Soybean, and the United Soybean Board) were conducted, one each in Franklin County, Hutchinson, Jefferson County, and Manhattan. For the 2017 season, two additional studies (a collaboration between K-State, Kansas Soybeans, and the North Central Soybean Research Program) were conducted in Ashland Bottoms near Manhattan and Franklin County.
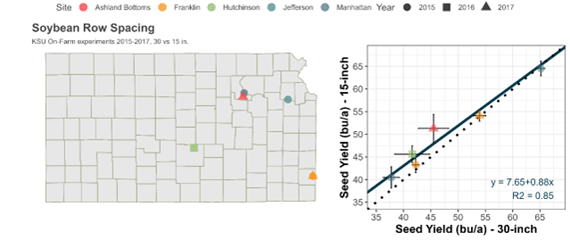
Figure 1. On-farm experiments on soybean row spacing comparing conventional (30-inch) vs. narrow rows (15-inch). Collaborators: Kansas State University, United Soybean Board, North Central Soybean Research Program.
Results summary
Compared to the conventional 30-inch row spacing, soybeans in narrow rows (15-inch or less) in these tests were likely to show equal or slightly greater yields (2-12%), particularly when the yield environment was less than 50 bushels per acre (Figure 1) (regardless of planting date, seeding rate, or maturity). Above this yield threshold level, soybeans did not show a yield response to changing the row spacing (Figure 2). Overall, the common denominator of the response to row spacing is the inconsistency, denoted by the wide error of responses and by the variability between site years.
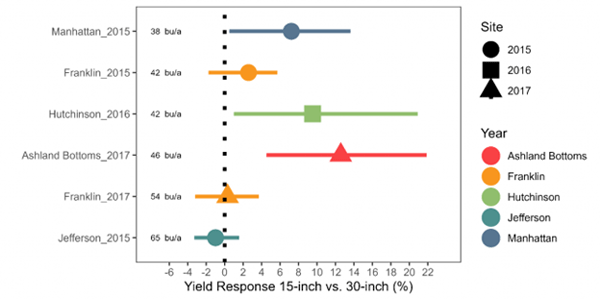
Figure 2. Observed yield response in soybeans to narrow rows (15-inch) compared to conventional spacing (30-inch). The average yield of 30-inch strips is indicated on the left side of the figure (bu/a). At the lowest-yielding site, Manhattan (2015), soybeans in 15-inch row spacing had an average of about 6% higher yields than those in 30-inch rows. In the highest yield environments, Jefferson County (2015) and Franklin County (2017), there was very little yield difference between 15- and 30-inch rows. On-Farm Experiments (2015-2017). Collaborators: Kansas State University, United Soybean Board, North Central Soybean Research Program.
Take home message
Benefits of narrow row spacing:
- Early canopy closure favors better light interception.
- Improved weed control.
- Reduced potential for soil erosion.
Disadvantages of narrow rows:
- Potential reductions in the final stand at a given seeding rate linked to equipment and within row compaction.
- In very dry years, narrow row spacing may consume limited soil water earlier in the growing season, reducing the amount of water available for the critical period around pod-setting and seed filling.
- In wet years, too narrow spacing (less than 15 inches) may allow less airflow within the canopy and favor the occurrence of certain diseases, such as white mold.
Ignacio Ciampitti, Farming Systems Specialist
ciampitti@ksu.edu
Ana Carcedo, Postdoctoral Fellow
carcedo@ksu.edu
Victor Gimenez, Postdoctoral Fellow
vgimenez@ksu.edu
Tags: soybeans row spacing