Southern corn rust continues to spread in the southern part of the US and is now detected in 7 counties across central and eastern Kansas (Figure 1). Unlike some other corn diseases, such as gray leaf spot, southern rust does not survive in Kansas during winter months and blows in annually from more tropical regions. The severity is dependent on the weather and southern rust likes 90-degree days, warm nights, and high humidity.
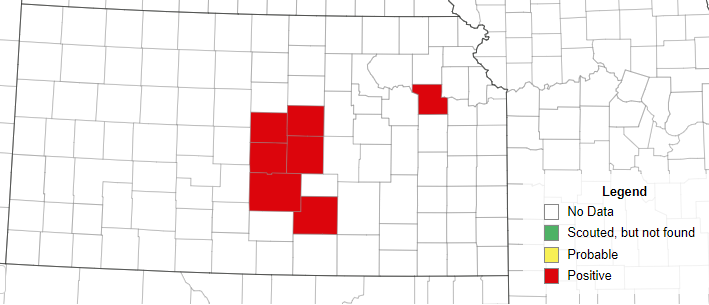
Figure 1. Southern corn rust (Puccinia polyspora) in Kansas as of August 10, 2023. Source: https://corn.ipmpipe.org/southerncornrust/
Here are some frequent questions related to managing southern rust in Kansas.
Q1. Should I apply a fungicide prior to observing southern rust?
A1. It is not recommended to apply a fungicide to control southern rust unless the disease has been observed in the canopy. Now that southern rust has been reported in Kansas, it is time to be out scouting corn fields. Once pustules are observed, the pathogen can reproduce rapidly if temperatures and humidity are high.
Q2. What factors should I consider when making the decision to spray for southern rust?
A2. It is important to consider hybrid susceptibility, disease incidence (how many plants are affected), and the growth stage of the crop. Infection early in the season on a susceptible hybrid, coupled with conducive weather conditions, pose the highest risk for yield loss.
Q3. If I apply a foliar fungicide at tasseling (VT) or silking (R1) to control gray leaf spot, will this application have efficacy against southern rust?
A3. Yes. Most fungicides that are labeled for gray leaf spot are also effective for southern rust and will have residual activity for approximately three weeks after application, depending on the product. Fields should be carefully monitored for disease development. Research has suggested that applications can be effective at preserving yield up until dent (R5) when dealing with a susceptible hybrid and high disease pressure.
Q4. What fungicides are best to control southern rust?
A4. Efficacy ratings for corn fungicide management of southern rust have been compiled by a working group of corn researchers and can be found here:
Q5. How do I know if what I’m seeing is southern rust?
A5. Southern rust produces characteristic orange pustules of spores, primarily on the upper side of the leaf (Figure 2). If you run your finger across the pustules, the orange spores will be visible on your hand. The Kansas State Plant Diagnostic Lab can also confirm southern rust by observing spores under the microscope. Additional information about sending in a sample can be found here: https://www.plantpath.k-state.edu/extension/diagnostic-lab/.
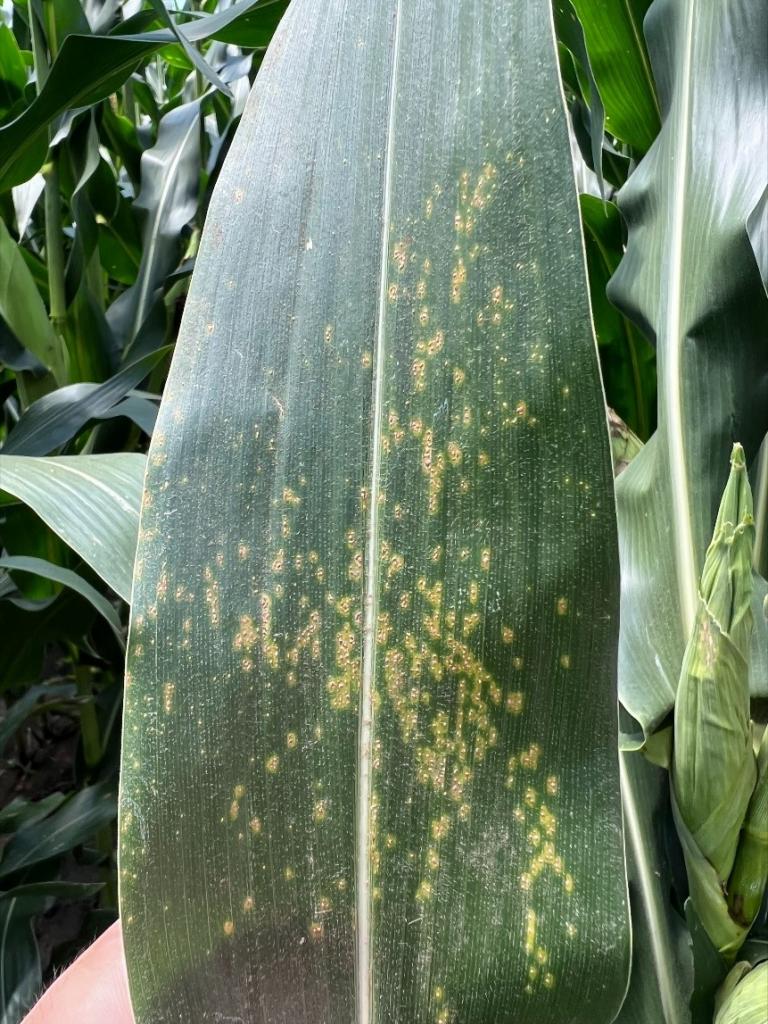

Figure 2. Southern rust on corn. Photo courtesy of Rodrigo Borba Onofre, K-State Plant Pathology.
For more information on identifying corn rusts, see K-State Research and Extension Bulletin MF3016, Corn Rust Identification and Management in Kansas.
Rodrigo Borba Onofre, Plant Pathology
onofre@ksu.edu
Tags: corn disease southern rust