The dry conditions throughout much of Kansas have led to an increased danger of wildfires. This is normally the time of year for prescribed burns on warm-season rangeland in eastern Kansas, so a wildfire at this time will not permanently harm the quality of vegetation on this kind of grazing land. However, a wildfire may act differently than a carefully planned prescribed burn. Should it produce enough heat it could cause damage, especially to bunch grasses, potentially resulting in a decline in productivity for a year or two. The best general advice for now on burned rangeland is to just wait and see how well it recovers. There are multiple management considerations for burned cropland depending on current or intended crop and other factors (Figure 1). There have also been questions about the effect of the wildfire or super-heated winds on soil quality and soil erodibility.
Figure 1. Wildfires can have many management implications for rangeland, cropland, and soil. Photos by Lucas Haag, K-State Research and Extension.
I. Effects on Rangeland and Management Strategies
Where a wildfire occurs, the ability of rangeland or tamegrass pastures to regenerate forage depends on precipitation amounts, the time of year that the fire occurs, the water infiltration ability of the soil, and management factors following the fire. Most of the soils in western Kansas were very dry going into the winter. The topsoil was generally quite dry at the time of the fire, and subsoil moisture was minimal. This will slow grass recovery and may take a few years to fully recover, depending on moisture during the growing season.
A previous wildfire in central Kansas that occurred in mid-March in a dry year on shortgrass rangelands reduced forage production 65% the year of the burn and 39% the following year. This shortgrass rangeland consisted primarily of blue grama, buffalograss, and western wheatgrass. In mixed prairie grassland, bunchgrasses such as little bluestem with large accumulations of dead plant material may be damaged as the passing fire ignites the dry material and generates increased temperatures at the soil surface for a period of time. If this occurs, forage production may be reduced by about 10-20 percent.
Wildfires tend to move rapidly, typically the result of high winds, low relative humidity, and warm air temperatures. Movement through rangeland grasses, especially those with rhizomes, is normally quick with reduced residence time. Therefore, there is an expectation that grasses should recover in time. Wildfires can also reduce stored carbohydrate reserves for grass plants, reduce moisture infiltration, increase evaporation and runoff, lead to erosion, create grazing distribution problems, and lead to an infestation of noxious weeds.
The crowns of grass plants often survive a wildfire and will regrow, but some can be damaged if the fire occurs when soil and air conditions are extremely dry. If plant litter remains after the fire, less damage will have occurred to the plant crowns, and soil conditions will be better. Evaporation and runoff may be increased if the fire occurs when the grasses are not actively growing. Bare soil may lose at least one-half inch of moisture per week through evaporation. The higher the clay content of the soil, the greater the potential for puddling and runoff.
Trees can burn quite hot, and for an extended period of time, if they catch fire. Eastern red cedar trees, among others, may be killed by a wildfire. On rangeland, this would normally be considered a good thing.
Good precipitation during the early growing season following the wildfire will hasten recovery and lessen the immediate impact of the fire.
A. Native warm-season grass rangeland
Between mid-March and June, wildfires generally do not reduce forage production as much as fires later in the year. However, if conditions are dry, regrowth will not occur and stocking rate must be reduced. Wildfires at this time may change plant composition of the grazing land.
When wildfires occur between late June and frost, the major consideration is to protect the plants from overuse. Immediate removal of the grazing animals is usually necessary. This will permit regrowth and allow plants to accumulate food reserves before winter. Wildfires occurring between fall and mid-March leave the soil bare until spring growth. Forage yields will be reduced, and a reduction is stocking rate is advised.
On sandy soils, blowouts (eroded areas) should be controlled as soon as possible. Mulching with manure, straw, or hay free of noxious weeds, along with reseeding can stabilize the blowout area. Fencing of blowouts will restrict livestock traffic and speed recovery.
Several grazing management options exist after a wildfire. If a wildfire occurs where prescribed burning is generally practiced, burn the areas that were untouched by the wildfire in late spring, when the desirable grass species have 1 to 1.5 inches of new growth. This will encourage grazing of the entire pasture. Observe where the animals are grazing, and use grazing distribution tools such as salt, mineral, and oilers to attract cattle to underutilized areas.
For forage plants to recover, it usually will be necessary to reduce stocking rates on the burned area.
|
Area |
Year after wildfire |
Stock at: |
|
Flint Hills and East |
1 |
75-85% |
|
|
2 |
Normal |
|
Central Kansas |
1 |
65-75% |
|
|
2 |
90-100% |
|
|
3 |
Normal |
|
Western Kansas |
1 |
50% |
|
|
2 |
75% |
|
|
3 |
Normal |
Note: During lengthy droughts, use lower stocking rates than those listed in the chart. The main concern is the inability of the plants to regrow. The plants must be given the opportunity for regrowth during drought.
If a wildfire occurs where prescribed burning is not practiced, management decisions should be based on when the grassland was burned, how much of it was burned, and where livestock water is located.
Example 1: If there is a livestock-watering source in both the burned and unburned portions of the grassland, divide the burned and unburned areas (using an electric fence, for example) and reduce the stocking rate in the burned area.
Example 2: If there is only one livestock-watering source in the grassland area, the decision is whether to manage the burned or the unburned area. If the unburned area is larger, separate the two areas with an electric fence and stock the unburned area at the normal rate. If the burned area is larger, either manage only the burned part by reducing the stocking rate or establish an alternate water source, fence the area, and reduce the stocking rate on the burned portion. If the sole watering source is in the burned portion, the unburned portion would not be utilized unless the area was fenced and another water source established or a lane is fenced off to allow watering from the unburned area.
Example 3: If only a small portion of the grassland is burned, fence it off and reduce the stocking rate on the unburned portion accordingly.
Example 4: In areas where prescribed burning is commonly practiced, a partial burn of one-third of the pasture may provide an opportunity to try patch-burn grazing. Livestock will concentrate on the recently burned area, but the next year a different third of the pasture is burned and the livestock will change their grazing habits. Patch-burn grazing will result in rotational grazing without using a fence.
Mowing unburned areas in the early spring can encourage livestock to move from the burned area. However, don’t mow in August or September. Early intensive grazing is another option for burned areas. Removing all livestock from the grassland by mid-July provides late-season rest and time for the desirable grasses to replenish root reserves.
B. Tamegrass hay meadows
Hay meadows burned by wildfires will probably produce less hay. To return hay meadows to their former production, cut the meadow in early to mid-July to allow regrowth and replenishment of root reserves.
II. Effects on Cropland and Management Strategies
A. Growing wheat
Wheat in the jointing stage or beyond can be injured by fire or super-heated air. This injury will be most severe on the edge of the field closest to the fire or super-heated air. It is not uncommon to have some injury to growing wheat on the edge of a field if the field is adjacent to a prescribed burn. The injury symptoms may be bleached or scorched leaves and possibly damaged growing points. The extent of injury from a wildfire depends on how quickly the fire moved through the field or around the field.
Research has found that the lethal high temperature for wheat is about 120 degrees F (J. Exp. Bot. (1984) 35 (11): 1603-1608. doi: 10.1093/jxb/35.11.1603 http://jxb.oxfordjournals.org/content/35/11/1603.short).
A wildfire can easily heat the air or the plants themselves to well over those temperatures, depending on the distance of the fire from the wheat, possibly resulting in irrecoverable damage to the affected plants.
Wildfire injury to wheat will most likely be quite variable through the field. The only way to accurately assess any possible injury is to slice open the stems and examine the growing points 10-14 days after the fire. As with freeze damage, if the growing point is green and turgid (crisp) and light green, it is fine. If it is white, off-white or yellowing and soft, it is damaged. If there was extensive damage, the ability of the wheat to recover will be similar to the ability to recover from spring freeze injury.
B. Fields where wheat stubble or row-crop residue has been burned off
In many instances, fields of wheat or row-crop residue that were to be seeded are left barren after a wildfire event. There are many considerations and options for how to manage these fields moving forward. The first consideration should be how to protect the field from potential wind and water erosion through the use of emergency tillage (details are presented later in this article).
Farmers generally have several options:
1. Summer-fallow the land until seeding of the winter wheat crop
2. Plant a summer cash crop
3. Plant a cover crop. Options may be limited by timing and amount of precipitation received after the wildfire.
Summer-Fallow: Summer-fallowing the land is a straight forward option, but with zero residue present to buffer erosion by wind and water, care should be taken to use tillage operations that maintain surface roughness as long as possible up until seeding time.
Planting a summer cash crop: As wildfires typically follow long periods without precipitation, it’s likely that little soil water exists in the profile. While profile water at planting is important, data from long-term rotation studies at Tribune have consistently shown that surface residue plays a very important role in maximizing the utilization of in-season precipitation. The reduced precipitation use efficiency combined with low levels of profile water make cropping with a summer cash crop a particularly risky option. The larger challenge then becomes if the cash crop fails without producing much above-ground biomass, the producer is then entering the typically dry, windy winter quite vulnerable to further wind erosion.
Planting a cover crop: If sufficient precipitation is received to establish a stand, a producer may consider a cover crop to grow some biomass as soon as possible and potentially serve as a feed resource if enough growth occurs. In general, a farmer should select species that offer the highest amounts of biomass production per inch of water consumed. For cool-season species, this would include triticale and cereal rye. Millets and sorghums are warm-season species. In the early spring, a producer may want to plant a blend of a cool-season and warm-season species to get some cover more quickly from the cool-season crop, followed by higher amounts and more durable residue from the subsequent warm-season crop.
Keep in mind that soil temperatures will be warmer with no residue, so millets and sorghums will generally germinate earlier than what is considered normal at a typical planting date. If planting a blend, it’s important to select a planting depth that both places the seed into moisture, but also is an acceptable depth for the species selected. Some potential cover crops such as oats and some millets will require shallower seeding than other potential species. At the time of this writing, most producers should consider moving towards seeding warm-season covers. If a producer has access to a hoe-drill, that method of seeding may offer some benefits for erosion reduction, protection of the emerging cover crop, and -- if done on the contour of sloping land -- reduction of soil erosion by runoff.
Nutrient considerations: About half of the nitrogen, and sulfur in the crop residues are lost to combustion during a fire. In extremely hot fires (the occurrence of white ash is an indicator) more than 25% of the phosphorus in the residue may be lost. Remaining nutrients would be in the ash, which can easily be lost from the field by wind or runoff. If nitrogen had been surface applied and was not yet incorporated by precipitation or tillage it is likely a significant portion will have been lost. It will take time for nutrient cycling to regain its normal function. It’s recommended that proper soil sampling be conducted prior to the next cash crop and thereafter so that deficiencies may be detected and addressed.
III. Effects on Soil
The number one issue regarding the impact of a wildfire on soil quality is going to be susceptibility to erosion from water or wind. Past research, mainly on forest soils after a fire, indicate there is nothing to worry about as far as long-lasting chemical or biological effects in the soil from a fire. Managers and landowners may notice a hardening of the soil surface, but there is no reason to be concerned that the fire will cause the soils to become hydrophobic. That can happen in forest soils, but is unlikely grassland soils. Any surface hardening caused by the wildfire will likely be shallow and temporary.
If the vegetative cover on the surface of the soil was completely burned off, this increases the potential for wind erosion during the early spring months, when wind erosion rates are often at their highest.
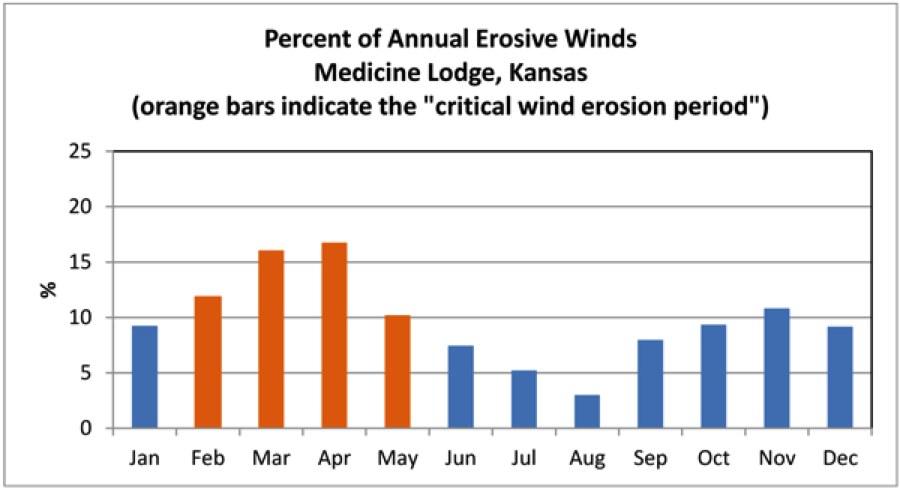
Source: John Tatarko, USDA-ARS Agricultural Systems Research Unit, Ft. Collins, Colo.
If the vegetation begins to regrow within a week or two, which may well occur on warm-season grasslands, this will reduce the potential for erosion problems. When vegetation or residue cover is insufficient, ridges and large soil clods (or aggregates) are frequently the only means of controlling erosion on large areas. In grasslands, seeding a temporary cover crop is another option for small areas, if the permanent grasses and forbs do not seem to be growing back two or three weeks after receiving some moisture. If there is no soil moisture, however, planting a cover crop will likely fail under this scenario.
Another option for cropland and smaller tracts of grassland left bare of vegetation or residue by the wildfire is to roughen the land surface with ridges and clods. This reduces the wind velocity and traps drifting soils. While this is not practical to do on large acreages of rangeland, it can be an effective practice on smaller acreages, and on cropland ground. A cloddy soil surface will absorb more wind energy than a flat, smooth surface. Better yet, a soil surface that is both ridged and cloddy will absorb even more wind energy and be even more effective in reducing the potential for wind erosion.
Crosswind ridges are formed by tilling or planting across the prevailing wind erosion direction. If erosive winds show no seasonal or annual prevailing direction, this practice has limited protective value. In Kansas, the prevailing winds in early spring the prevailing winds are from the south. Crosswind ridges at this time of year, therefore, should be in an east-west direction to protect from both northerly and southerly winds.
When cropland and grasslands were both burned and border each other, it’s useful to create ridges along the field boundaries, to help prevent the drifting of soil into the fencerow area or adjoining road ditches. In sloping fields with contour conservation terraces, continuous east-west or southeast-northwest passes may not be possible. In these cases, a farmer may consider using tillage to roughen the terrace faces that have the greatest exposure to predominant winds with additional tillage passes on the contour in-between terraces if blowing continues. Additionally, contour tillage on terrace backsides and in-between terraces may reduce potential soil movement due to precipitation run-off until surface residues can be regrown.
Tillage implements can form ridges and depressions that alter wind velocity. The depressions also trap saltating soil particles and stop avalanching of eroding material downwind.
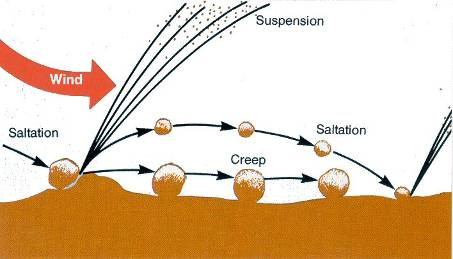
Source: Principles of Wind Erosion and Its Control, K-State Research and Extension publication MF-2860: http://www.bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF2860.pdf
However, soil ridges protrude higher into the turbulent wind layer and are subject to greater wind forces. Therefore, it is important that cloddiness on top on the ridge is sufficient to withstand the added wind force, otherwise they will quickly erode, and the beneficial effects will be lost. Ridging sandy soils, for example, is of little value because the ridges of sand are erodible and soon leveled by the wind.
Clod-forming tillage produces aggregates or clods that are large enough to resist the wind force and trap smaller moving particles. They are also stable enough to resist breakdown by abrasion throughout the wind erosion season.
If clods are large and stable enough, as smaller particles are removed or trapped, the surface becomes stable or “armored” against erosive action. The duration of protection depends on the resistance of the clods to abrasion or changes in the wind direction.
Of the factors that affect the size and stability of soil aggregates, most notable is soil texture. Sandy or coarse-textured soils lack sufficient amounts of silt and clay to bind particles together to form aggregates. Such soils form a single-grain structure or weakly cemented clods, a condition that is quite susceptible to erosion by wind. Loams, silt loams, and clay loams tend to consolidate and form stable aggregates that are more resistant to erosive winds. Clays and silty clays are subject to fine granulation and more subject to erosion. Another factor is moisture; if a soil is totally dry, there may not be enough moisture for clod-forming tillage, or you may need to go deeper.
Selection of the proper tillage implement for emergency tillage is critical to produce meaningful and lasting effects. Chisels, aggressive rippers, and listers are useful implements when they can be ran deep enough to bring large clods to the surface. Any type of rolling basket or firming wheels on a ripper or harrows on a chisel, should be completely raised to maximize surface roughness. Sweep (blade) plows, field conditioners, discs, and vertical tillage machines are not useful in reducing wind erosion and in many instances can make the situation worse by exposing even more fine, erodible, soil particles than would be exposed on a post-fire soil surface.
For more information, see:
Rangeland Management Following Wildfire, K-State Research and Extension publication L-514 at: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/Item.aspx?catId=364&pubId=385
Principles of Wind Erosion and Its Control, K-State Research and Extension publication MF-2860 at: http://www.bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF2860.pdf
Emergency Wind Erosion Control, K-State Research and Extension Publication MF-2206 at: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/mf2206.pdf
Walt Fick, Rangeland Management Specialist
whfick@ksu.edu
Lucas Haag, Northwest Area Crops and Soils Specialist
John Holman, Southwest Research-Extension Center Agronomist
DeAnn Presley, Soil Management Specialist
deann@ksu.edu
Romulo Lollato, Wheat and Forages Specialist
lollato@ksu.edu
Chip Redmond, Kansas Mesonet Manager