More Kansas farmers are using late-planting dates to diversify production risks; however, final planting dates for crop insurance eligibility provide a limit for late planting. Planting corn later in the season increases the chances of receiving late-summer rains and reduces the effect of heat stress during flowering. The lack of information about late planting makes it difficult to make management decisions concerning this practice.
A recent study was conducted at Kansas State University with the following objectives:
- Define corn-yield environments based on grain-yield levels and stability over time.
- Explore different combinations of hybrid maturity by planting date and the effects of these combinations on final corn yields.
- Quantify the season-ending frost-risk effect of delaying planting dates on yield.
Two sources of information were summarized for this study: a field study conducted to obtain detailed life cycle (crop phenology) data for corn, and crop simulations to transfer the approach to other regions. Corn yield environments were defined by grouping the mean yield and its corresponding standard deviation based on 30 years of weather data (Figure 1).
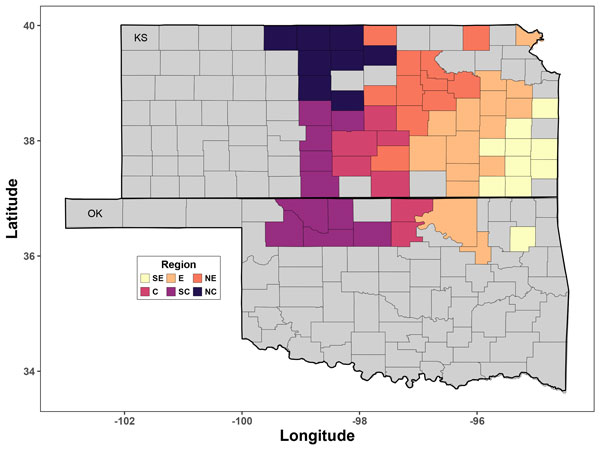
Figure 1. Corn productivity regions for counties across Kansas and Oklahoma. Map from KSRE publication MF3610.
Results
Corn yield environments were defined across the state considering the optimal combination of hybrid maturity and planting date. The groupings were defined by clustering the mean yield and its corresponding standard deviation based on 30 years of weather data (Figure 1). Greater yields were attained with long-maturity hybrids (comparative relative maturity, CRM > 100).
Planting dates after mid-May decreased yields in eastern Kansas (Figure 2). In the central and south central regions, corn yields remained stable from early- to late planting dates (April 1 to July 1), but significantly increased the risk of frost damage, with effects on yields, after June 15.
The north central region presented similar corn yields for rain-fed conditions when planted early (April 1) until late-planted times. After June 1, the frost risk increased up to 25%. Thus, late May/early June dates combined both adequate yields with low frost risk.
Similar scenarios are reported for the northeastern area, with corn yields under rain-fed conditions remaining stable but increasing the risk of freeze damage for mid-June planting dates (20%).
Comparable to the northeastern area, in the southeast region, corn yields were reduced with delays in planting date, with the major frost risk defined after June 15.
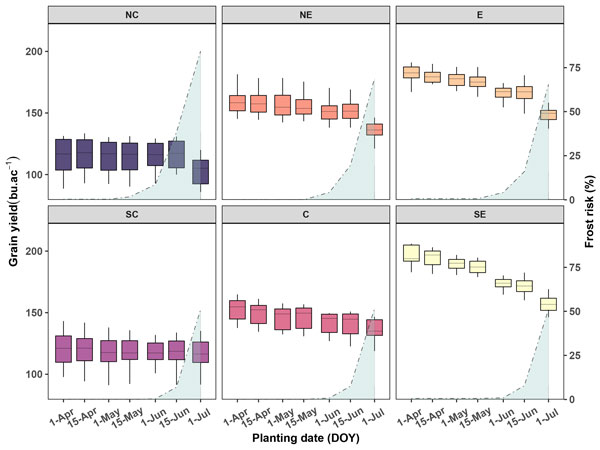
Figure 2. Corn grain yield (bu/a) and frost risk (i.e., risk percentage of having a frost (32°F) before physiological maturity for 30-year weather data) as a function of planting date (April 1, April 15, May 1, May 15, June 1, June 15, and July 1) for a hybrid comparative relative maturity of 101 in six regions across Kansas. Graphs from KSRE publication MF3610.
Summary
Opportunities for increasing yields and/or the number of crops per year were demonstrated mainly in the central and south central regions, either by:
- Delaying planting date to early- to mid-June (without any clear yield penalty) and including a cover crop for spring time (before the summer crop option), or
- Planting early (April), allows harvesting the crop by mid-September, following up with a winter crop option (e.g., winter wheat or canola).
This information is critical to re-evaluating the final planting dates and redefine the planting window for corn in Kansas.
This article was taken from the KSRE publication MF3610: Corn Planting Dates and Frost Risk in Central and Eastern Kansas. It is available online at: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/MF3610.pdf
This project is supported by Agriculture and Food Research Initiative Competitive Grant no. 2019-68012-29888 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture
Ignacio Massigoge, Graduate Student – Ciampitti Lab
imassigoge@ksu.edu
Ana Julia Paula Carcedo, Postdoctoral Fellow – Ciampitti Lab
carcedo@ksu.edu
Ignacio Ciampitti, Farming Systems
ciampitti@ksu.edu
Tags: corn planting date